User-defined kernels
The standard kernels in our JupyterHub setup include Python 3.6 and R 3.6.3, both with only few packages installed. These are sufficient for demonstration purposes, but may not contain specific packages that you may require. As a solution, you may set up your own kernel based on one of your local environments.
We will illustrate this process for both a MiniConda-installed Python and R environment. Please consult the VscDocumentation page on Python package management or the VscDocumentation page on R package management for MiniConda installation instructions.
Environment creation: Python
We will create a MiniConda environment with the following Python packages:
python 3.9numpyscipypandastensorflow-gpuipykernel
NOTE: Instead of creating a new environment you can also introduce an existing environment to your JupyterHub. In this case you can skip the creation of the environment. NOTE: Always include the ipykernel package in your environment, as this is necessary to install the kernel.
- Create a new Conda environment (here named
p39env):conda create -n p39env python=3.9 numpy scipy pandas tensorflow-gpu ipykernel - Activate the environment:
conda activate p39env - Install the associated IPython kernel in
${VSC_HOME}/.localso that JupyterHub can find it:python -m ipykernel install --prefix=${VSC_HOME}/.local/ --name 'p39env' -
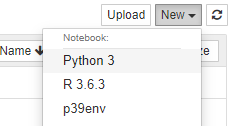
Connect to JupyterHub and verify that the new ‘p39env’ kernel appears. It should look like this:
- Test the environment and make sure that it works as expected.
Environment creation: R
For R, let’s create an environment with following packages, and let’s name it r41env:
R 4.1data.tableggplot2factoextrairkerneljupyter_client
NOTE: Instead of creating a new environment you can also introduce an existing environment to your JupyterHub. In this case you can skip the creation of the environment. NOTE: Always include the jupyter_client and the irkernel package, to be able to install the kernel.
- Create the new R environment:
conda create -n r41env r-base=4.1 r-data.table r-ggplot2 r-factoextra r-irkernel jupyter_client -c conda-forge - Activate the environment:
conda activate r41env - Install the kernel in
$VSC_HOME/.localto be able to use it in JupyterHub:Rscript -e 'IRkernel::installspec(prefix="${VSC_HOME}/.local/", name="r41env", displayname="r41env")' - Connect to JupyterHub and verify if you can find your newly created R environment in the kernel list.